active learning
"Machine learning force fields (MLFF), compared to traditional methods, can predict material properties and reaction mechanisms faster and more accurately. The current state-of-the-art deep learning-based molecular dynamics can simulate systems with billions of atoms. However, due to the interpolation nature of machine learning methods, MLFFs struggle to make accurate predictions in the phase space outside the training set. Since training data is usually generated using expensive first-principles calculations, it is challenging to obtain a large amount of ab initio data that is both representative and independent of extensive calculations. Improving the extrapolation capability of MLFF models without relying on a large amount of ab initio data is crucial. PWact (Active learning based on PWMAT Machine Learning Force Field) is an open-source automated active learning platform based on PWMLFF, designed for efficient data sampling."
AL-PWMLFF
The AL-PWMLFF platform consists of two main components: the main task and the task scheduler, as shown in the architecture diagram.
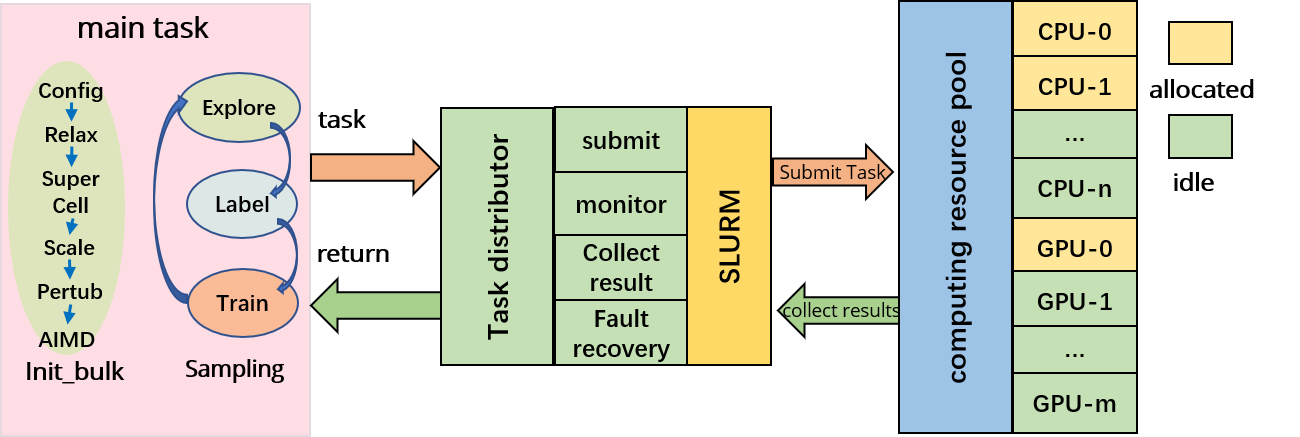
The main task includes two modules, preparing pre-training data (init_bulk) and active learning (sampling). It is responsible for generating computational tasks and collecting results during the preparation of pre-training data and the active learning process. The task scheduler receives task scheduling requests and assigns tasks to the corresponding computing nodes based on the resource utilization and task resource requirements. After the tasks are executed, the task scheduler collects the execution results from the computing nodes and returns them to the main task program.
pre-training data preparation module
Includes four sub-modules: relaxation (supporting PWMAT, VASP, CP2K), supercell generation, lattice scaling, lattice perturbation, and running MD (supporting PWMAT, VASP, CP2K). It also supports combinations of these modules.
active learning module
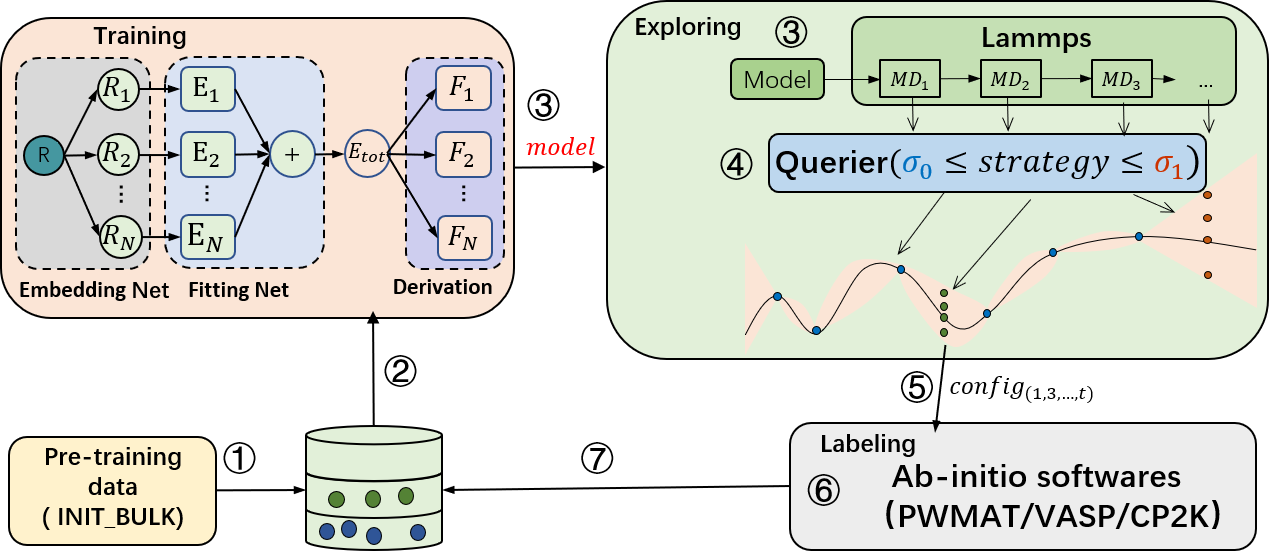
The active learning module consists of three sub-modules: training, configuration exploration, and annotation (supporting PWMAT, VASP, CP2K). First, the training module performs model training. Then, the trained model is passed to the exploration module, which uses the force field model for molecular dynamics simulations. After the simulation, the molecular motion trajectory is passed to the query module for uncertainty measurement. Once the query is completed, the annotated configuration points are sent to the annotation module. Finally, the annotation module performs self-consistent calculations to obtain energy and forces, which are used as labels along with the corresponding configurations in the annotated database. This process is repeated until convergence.
-
For model training, PWMLFF supports DP model, DP model with compress, DP model with type embedding and NEP(NEP4) model.
-
For uncertainty measurement, common methods based on multiple-model committee queries are provided, as well as our latest design, the single-model Kalman Prediction Uncertainty (KPU) based on Kalman filtering. This method can reduce the computational cost of model training to 1/N, where N is the number of models in the committee query, while achieving accuracy close to the committee query. Users are welcome to try this method. For the KPU method, it is only applicable to the DP model.
-
For annotation, PWMAT or VASP is supported.
The pre-training data preparation module
It includes four sub-modules: relaxation (supporting PWMAT, VASP, and CP2K), supercell generation, lattice scaling, lattice perturbation, and running MD (PWMAT, VASP, and CP2K). It also supports combinations of these modules.
Dependencies
-
AL-PWMLFF job scheduling uses the SLURM cluster management and job scheduling system. SLURM must be installed on your computing cluster.
-
AL-PWMLFF model training is based on
PWMLFF. Refer to thePWMLFF documentationfor installation instructions .
- AL-PWMLFF Lammps molecular dynamics simulation is based on Lammps_for_pwmlff. Refer to the
Lammps_for_pwmlff documentationfor installation instructions.
Installation Guide
PWact supports two installation methods: pip command installation and source code installation.
1. Pip Command Installation
Source Code Download
git clone https://github.com/LonxunQuantum/PWact.git
or
git clone https://gitee.com/pfsuo/pwact.git
The Gitee repository may not be updated as promptly as GitHub, so it is recommended to download from GitHub.
After downloading the source code, navigate to the root directory (at the same level as setup.py) and run the following command:
pip install .
# Or use the developer option, which installs without copying files. It reads directly from the source files, meaning any changes to the source code will take effect immediately. This is useful for users who need to modify the source code themselves.
# pip install -e .
PWact is developed in Python and supports Python 3.9 and above. It is recommended to use the Python runtime environment of PWMLFF directly.
If you need to create a separate virtual environment for PWact, you only need to install the following dependencies (matching your Python version, supporting Python 3.9 and above).
pip install numpy pandas tqdm pwdata
Command List
PWact includes the following commands, starting with the command pwact.
1. Output a list of available commands
pwact [ -h / --help / help ]
You can also use this command to check if PWact is installed successfully.
2. Output the parameter list for cmd_name
pwact cmd_name -h
3. Prepare initial training set
pwact init_bulk param.json resource.json
4. Active Learning
pwact run param.json resource.json
For the above two commands, the names of the json files can be changed by the user, but the order of input for param.json and resouce.json must remain the same.
5. Tool Commands
gather_pwdata
Searches all structures explored under the active learning directory and converts the results into a pwmlff/npy format training set.
pwact gather_pwdata -i .
Here, -i specifies the path to the active learning directory.
kill
Terminates an ongoing init_bulk task, such as relaxation (relax) or AIMD tasks.
# Navigate to the directory where the pwact init_bulk command was executed
pwact kill init_bulk
Terminates an ongoing run task, including running training, exploration (MD), or labeling tasks.
# Navigate to the directory where the pwact run command was executed
pwact kill run
The above kill commands can also be replaced by manual operations. First, terminate the main process executing pwact init_bulk or pwact run. Second, manually end the ongoing SLURM tasks.
To avoid accidentally terminating other processes, it is recommended to use the commands for termination.
After using the command to terminate processes, it is recommended to review the command output and use SLURM commands to check for any remaining processes.
filter
Test the point selection under specified lower and upper limits.
pwact filter -i iter.0000/explore/md -l 0.01 -u 0.02 -s
This command will analyze the selection results from all trajectories explored in the iter.0000/explore/md directory using a lower limit of 0.01 and an upper limit of 0.02 (as shown in the example below). The -s option is optional and specifies whether to save detailed selection information.
Image select result (lower 0.01 upper 0.02):
Total structures 972 accurate 20 rate 2.06% selected 44 rate 4.53% error 908 rate 93.42%
Select by model deviation force:
Accurate configurations: 20, details in file accurate.csv
Candidate configurations: 44
Select details in file candidate.csv
Error configurations: 908, details in file fail.csv
Input Files
AL-PWMLFF requires two input files, param.json and resource.json, for initial dataset preparation or active learning. AL-PWMLFF is not sensitive to the case input of keys in two JSON files.
param.json
Initial Training Set Preparation - init_param.json
Configurations (VASP, PWMAT format) for relaxation, supercell, scaling, perturbation, and AIMD (PWMAT, VASP, CP2K) settings.
Active Learning - run_param.jso
Training settings (network structure, optimizer), exploration settings (LAMMPS settings, sampling strategies), and labeling settings (VASP/PWMAT self-consistent calculation settings).
resource.json
Settings for computational cluster resources, including computing nodes, CPU, GPU resources for training, molecular dynamics (MD), DFT calculations (SCF, Relax, AIMD), and corresponding software (LAMMPS, VASP, PWMAT, PWMLFF).